Acanthurus mata (Cuvier, 1829)
Description
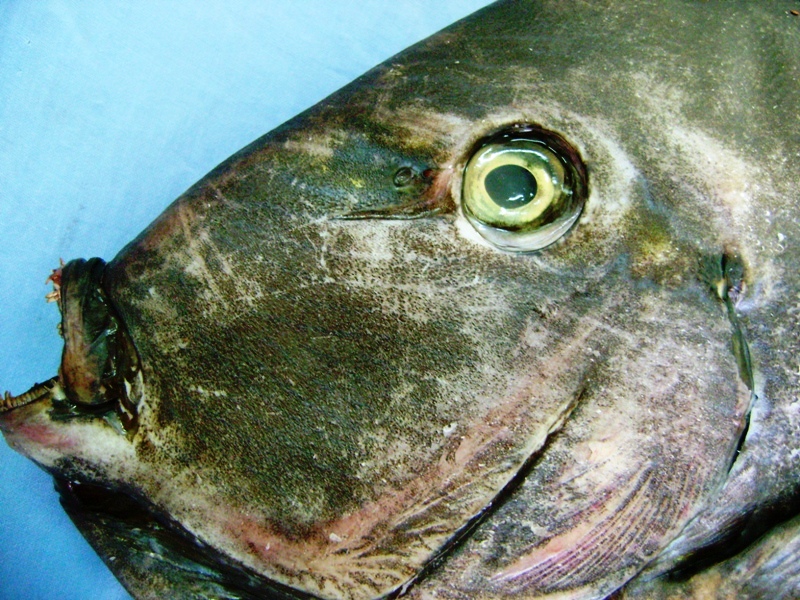
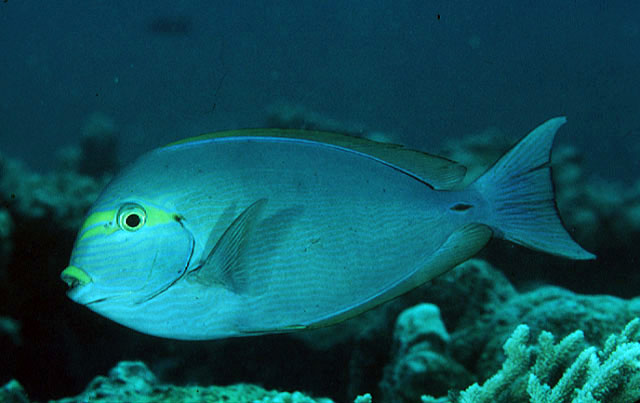
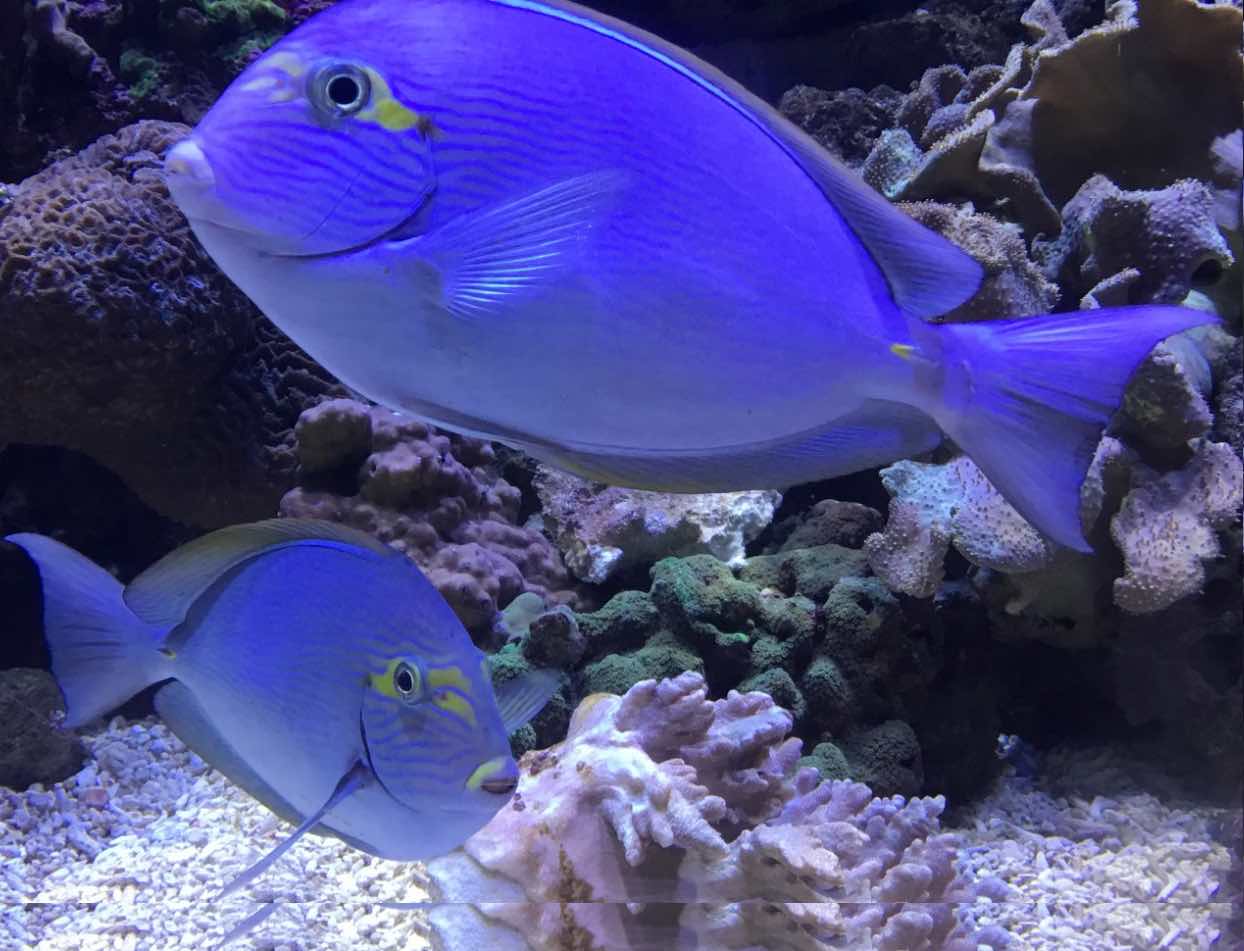
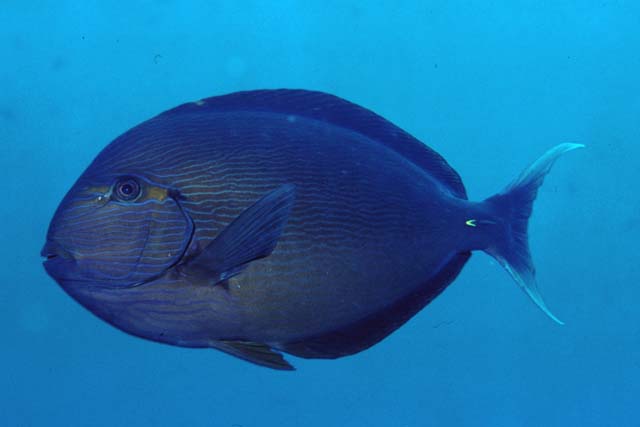
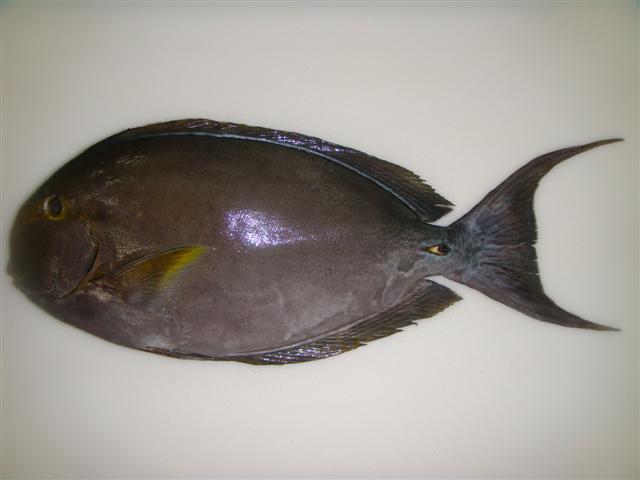
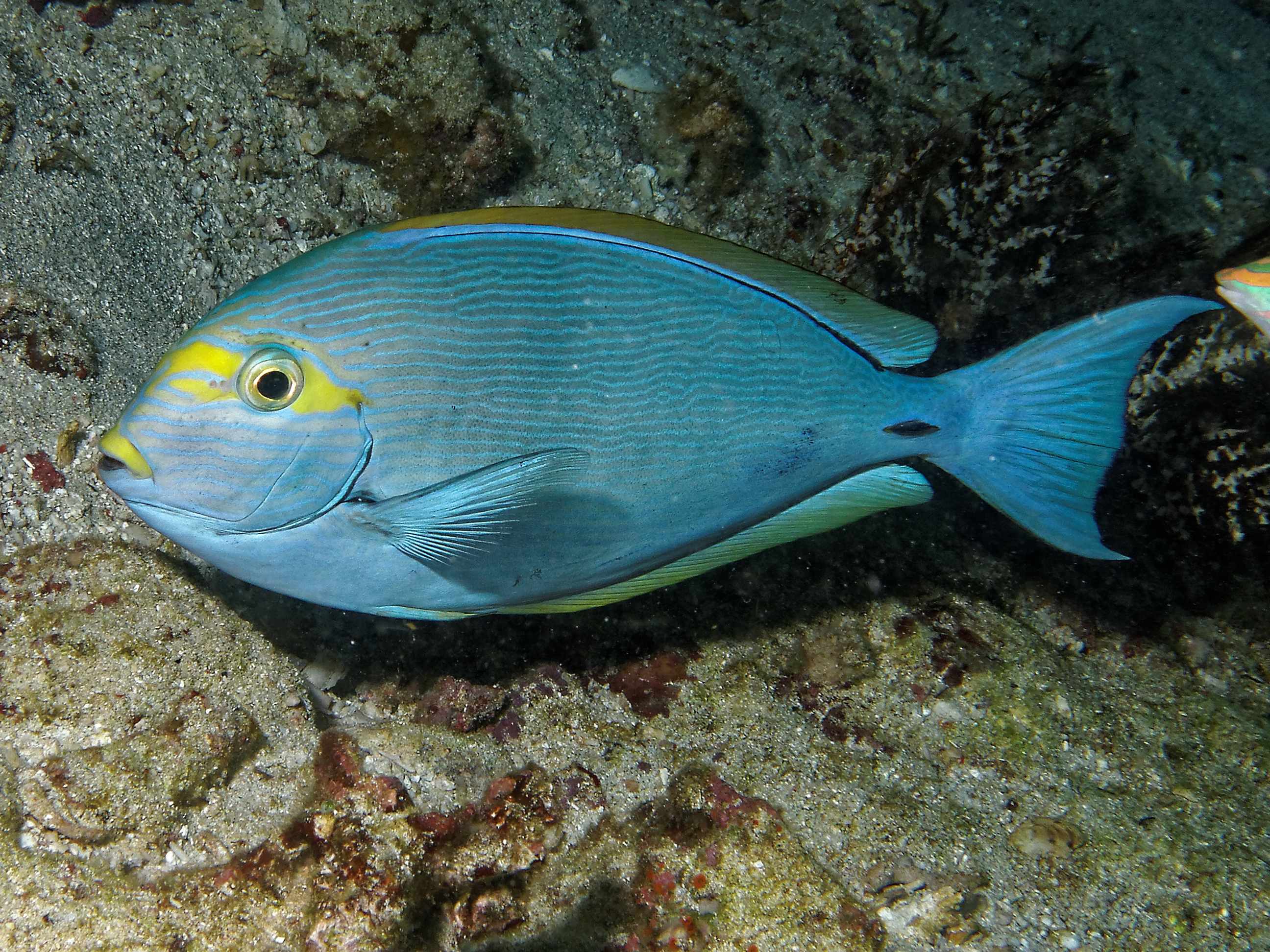
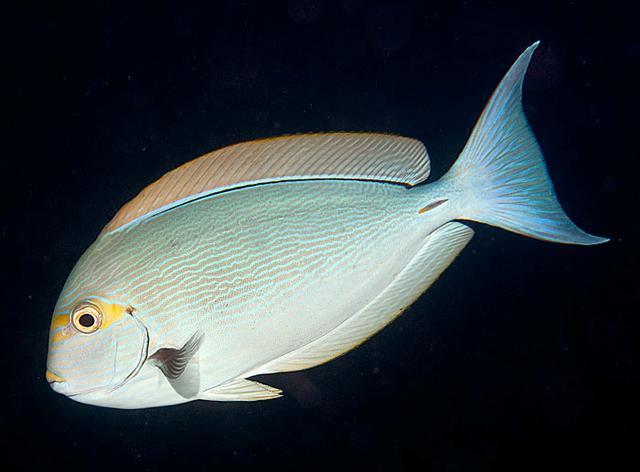
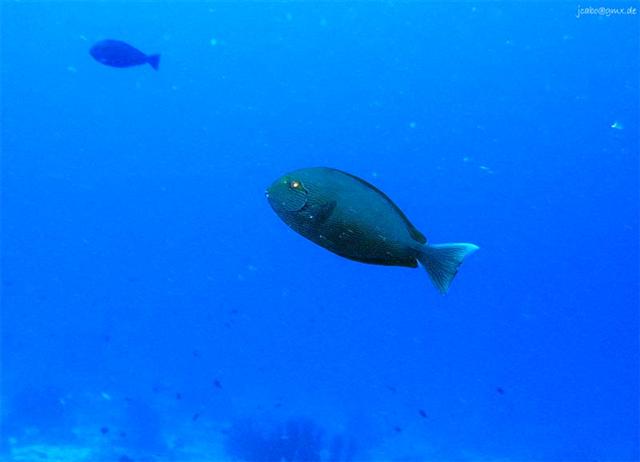
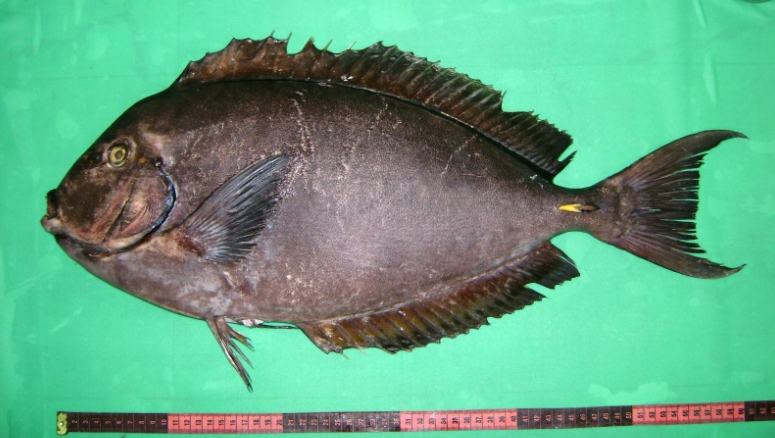
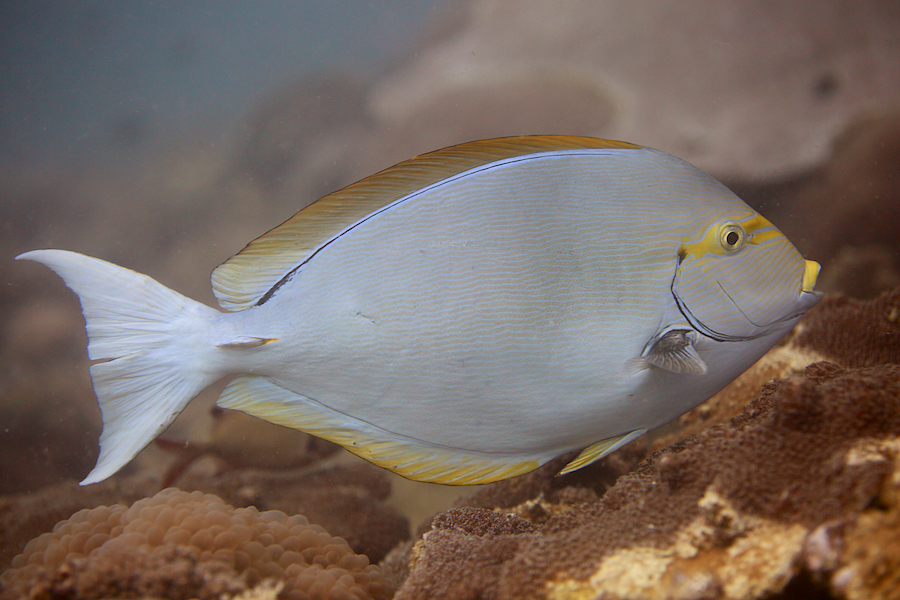
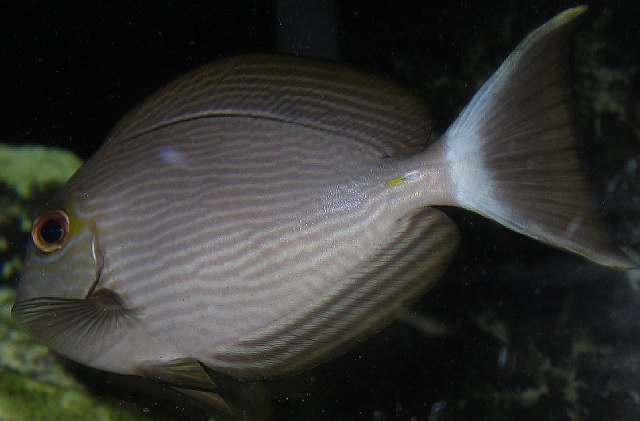
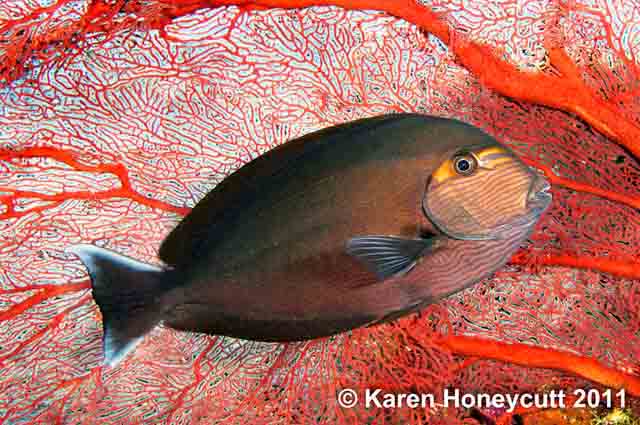
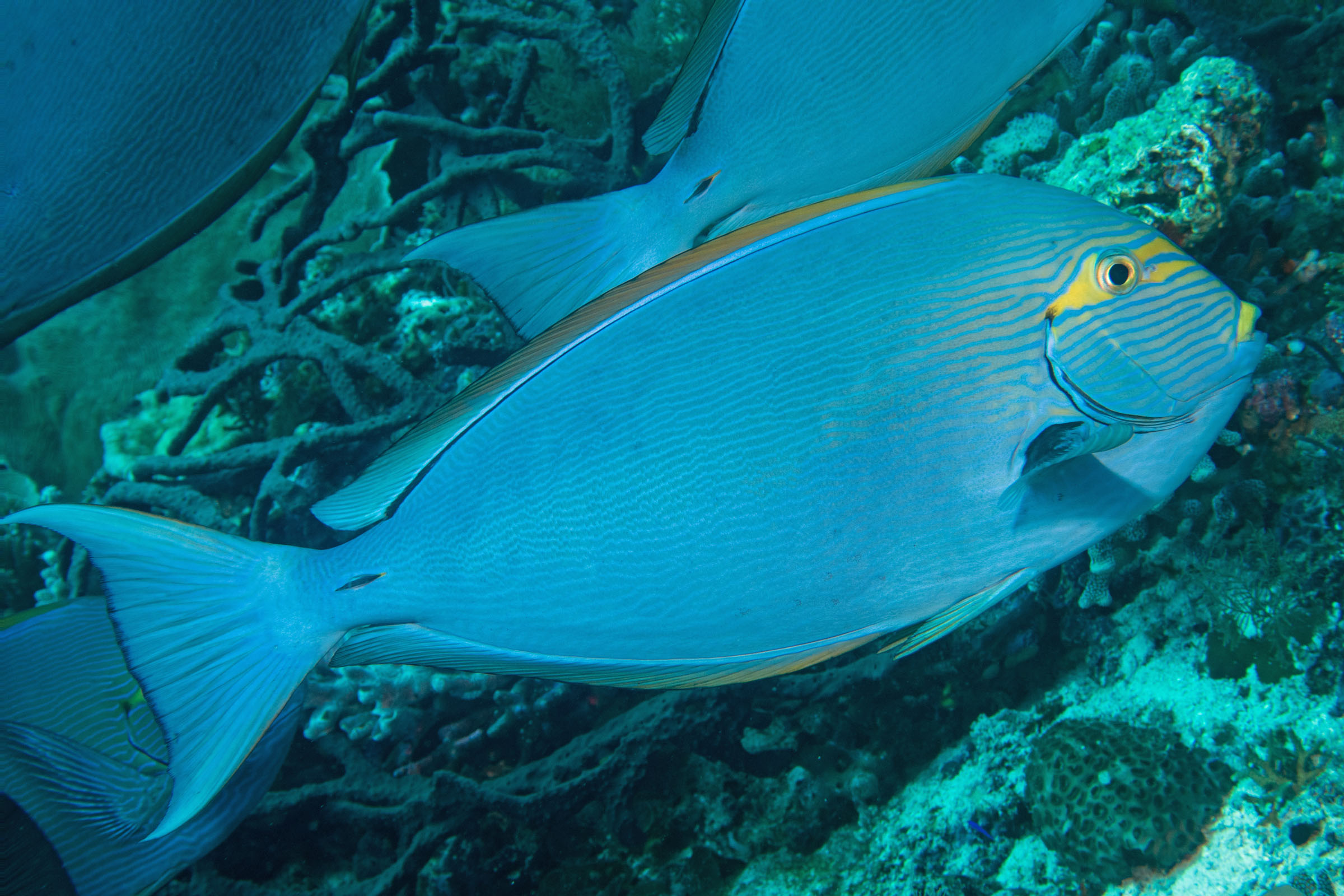
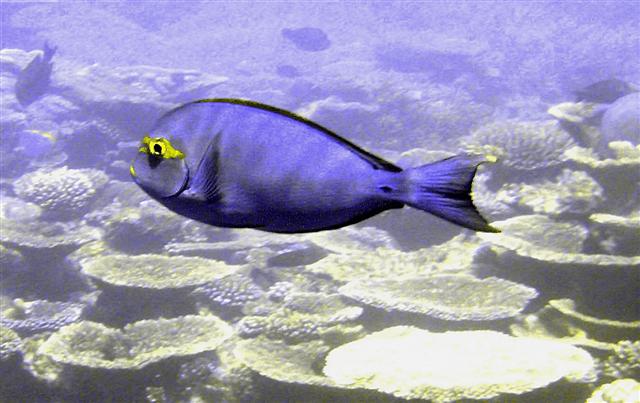
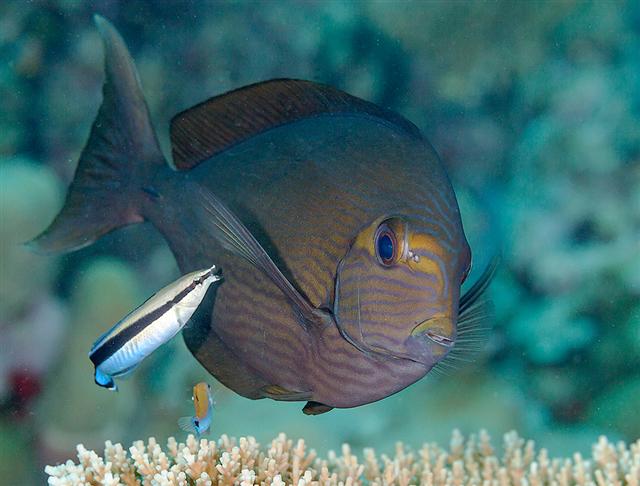
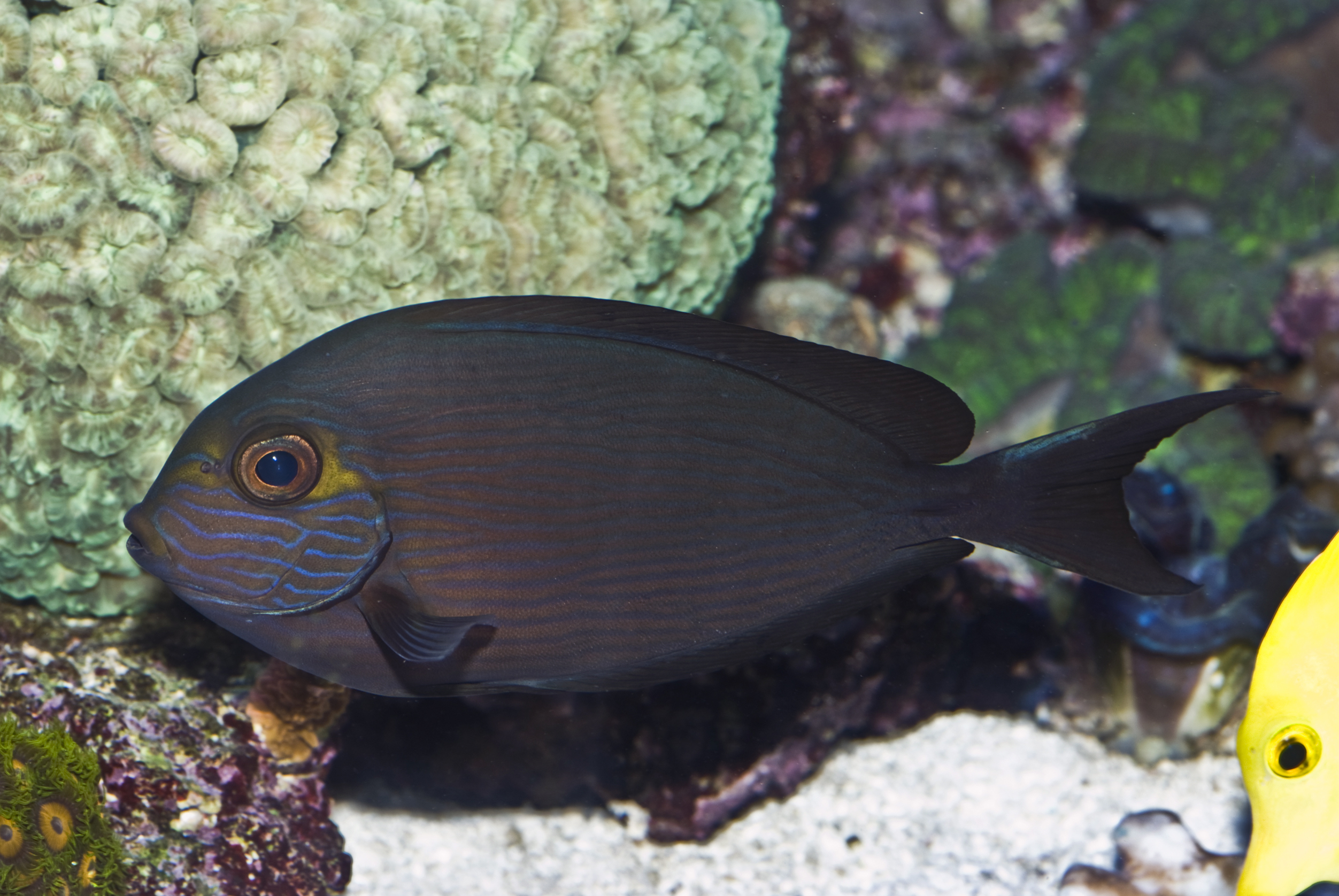
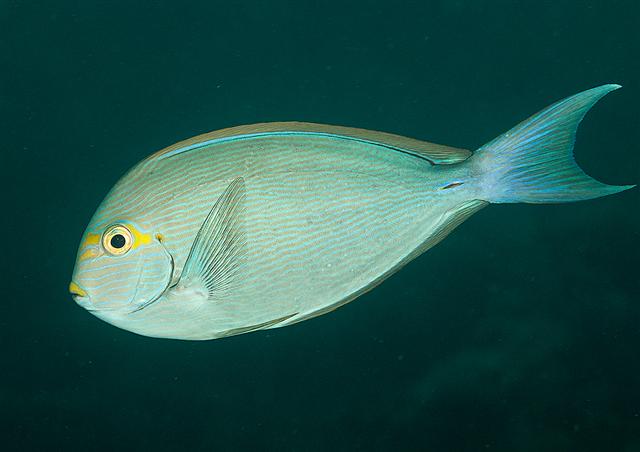
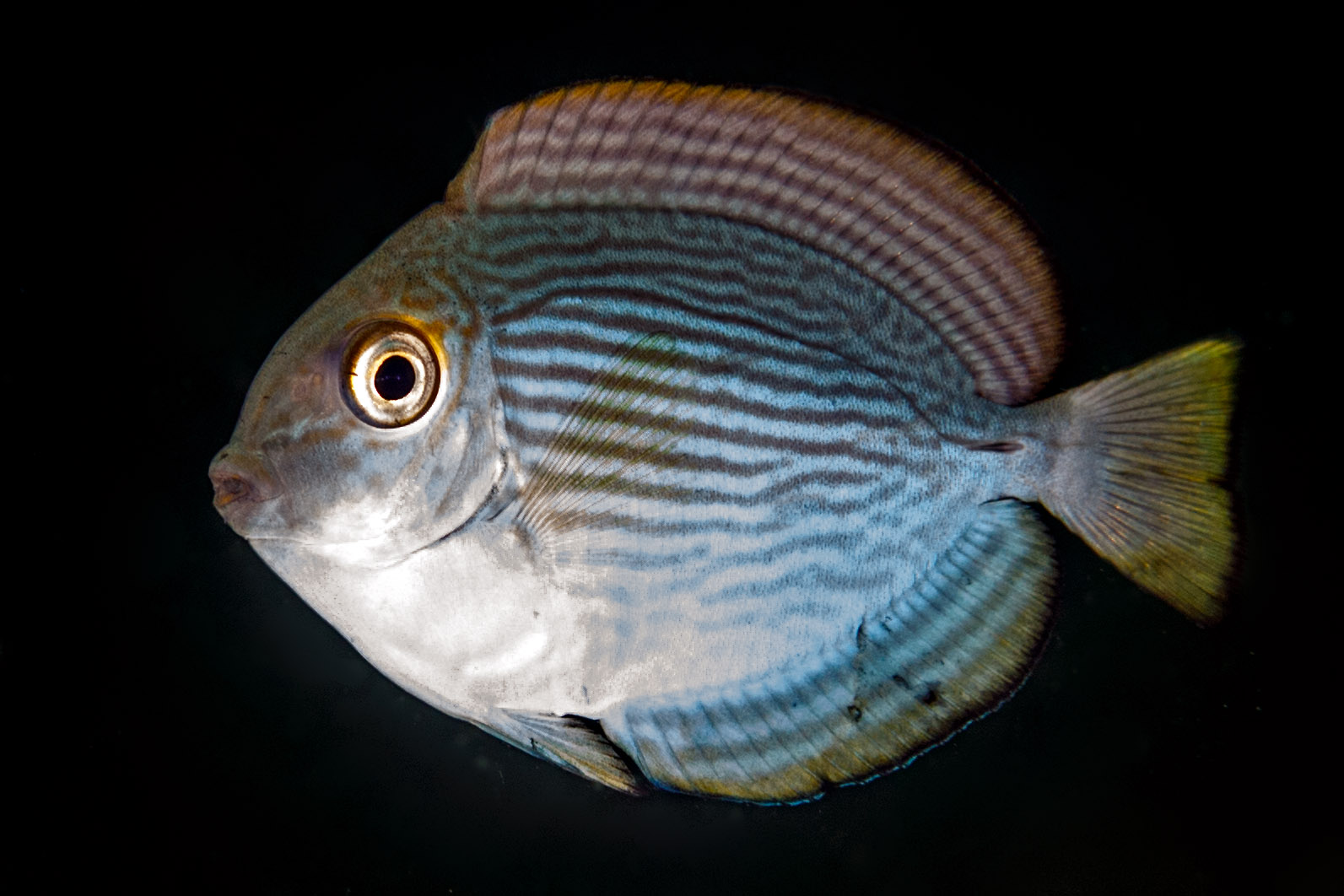
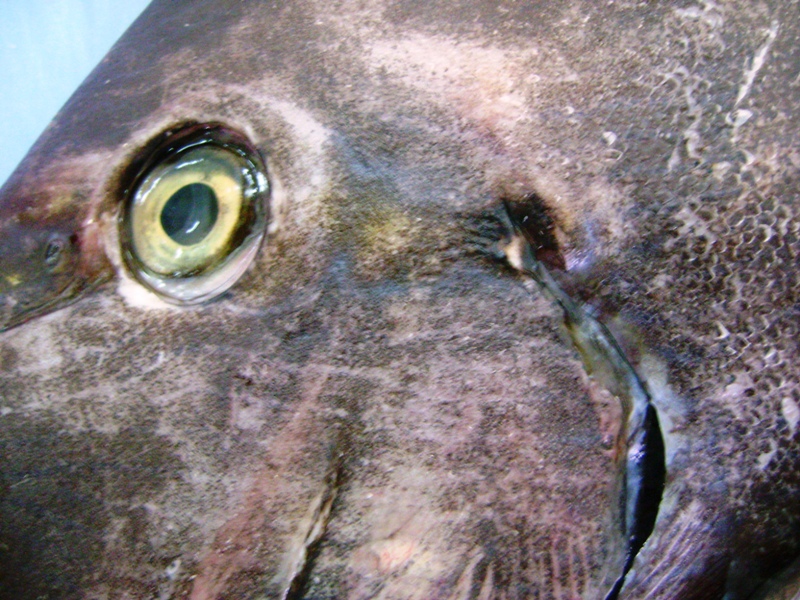
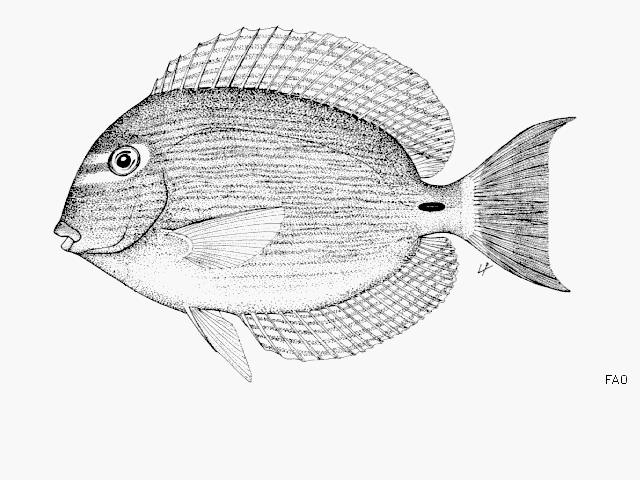
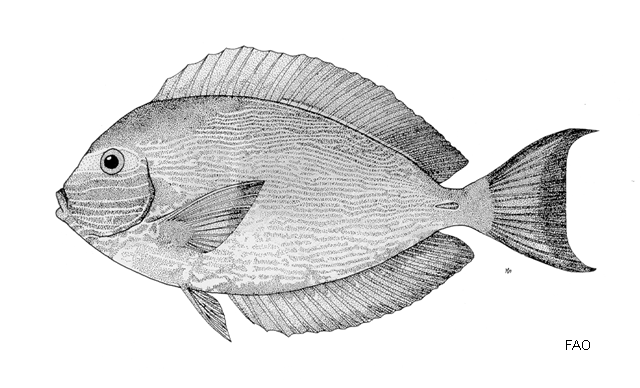
Dorsal spines (total): 9; Dorsal soft rays (total): 24 - 26; Anal spines: 3; Anal soft rays: 23 - 24. This species is distinguished by the following characters: body moderately deep and compressed, its depth 2.1-2.5 times in standard length or SL (smaller individuals are deeper-bodied); snout relatively short, 6-6.9 times in SL; eye 3.2-4.5 times in head length (at 12-28 cm SL); mouth small; teeth spatulate, close-set, with denticulate edges, and small for the genus; total gill rakers on first gill arch 13-15; continuous, unnotched dorsal fin IX,24-26; A III,23-24; caudal fin emarginate to lunate, concavity 6.5-9 times in SL (concavity is greater in larger individuals); caudal peduncle narrow, the least depth 10-12 times in SL with a lancet-like spine on each side which folds into a deep horizontal groove; stomach large, U-shaped, thin-walled with large, thorn-like papillae on inner surface; colour brown with longitudinal blue lines on head and body; a yellow area behind eye and 2 yellow bands extending anteriorly from eye; when alive, this fish is capable of changing its ground colour from dark brown to pale blue (Ref. 9808).
Common Names
No common names available.
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Teleostei
Order: Acanthuriformes
Family: Acanthuridae
Genus: Acanthurus
Species: Acanthurus mata (Cuvier, 1829)
Climate Zone
Location
Biology
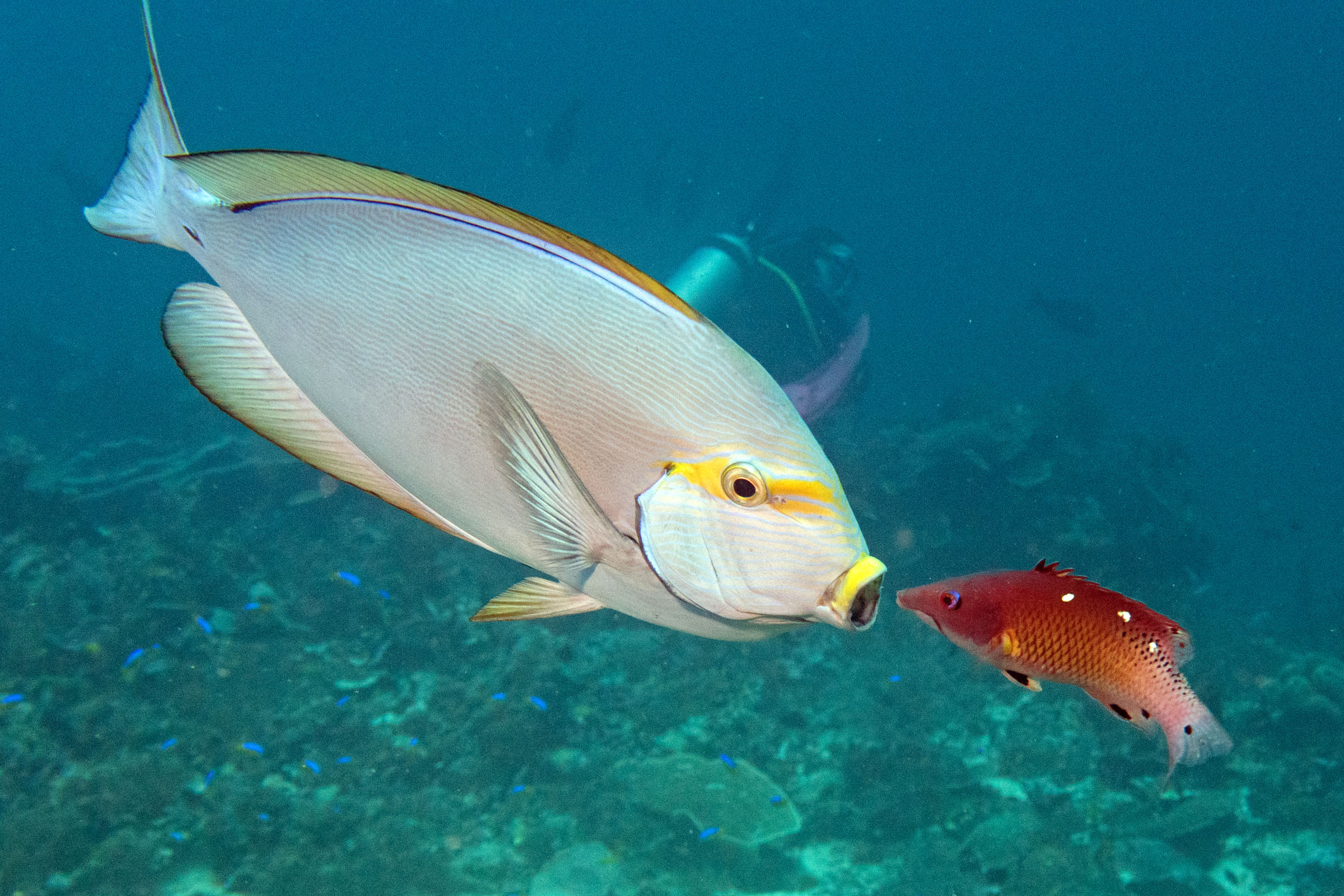
Adults inhabit steep slopes, often in turbid waters, generally in the vicinity of coral reefs (Ref. 58652) or rocky bottoms. They form resident spawning aggregations (Ref. 27825, 48637). Adults often seen in schools, feeding mid-water on plankton (Ref. 48637). Feed on zooplankton. Marketed fresh. Flesh is almost never poisonous (Ref. 4795), but incidence of ciguatera poisoning was reported from Nauru I. (Ref. 125620). The retractile sharp blades of the caudal peduncle can be dangerous (https://www.monaconatureencyclopedia.com/acanthurus-mata-2/?lang=en, ver. 12/2021)
Habitat
associated
Conservation Status
Least Concern
Threat to Humans
Traumatogenic