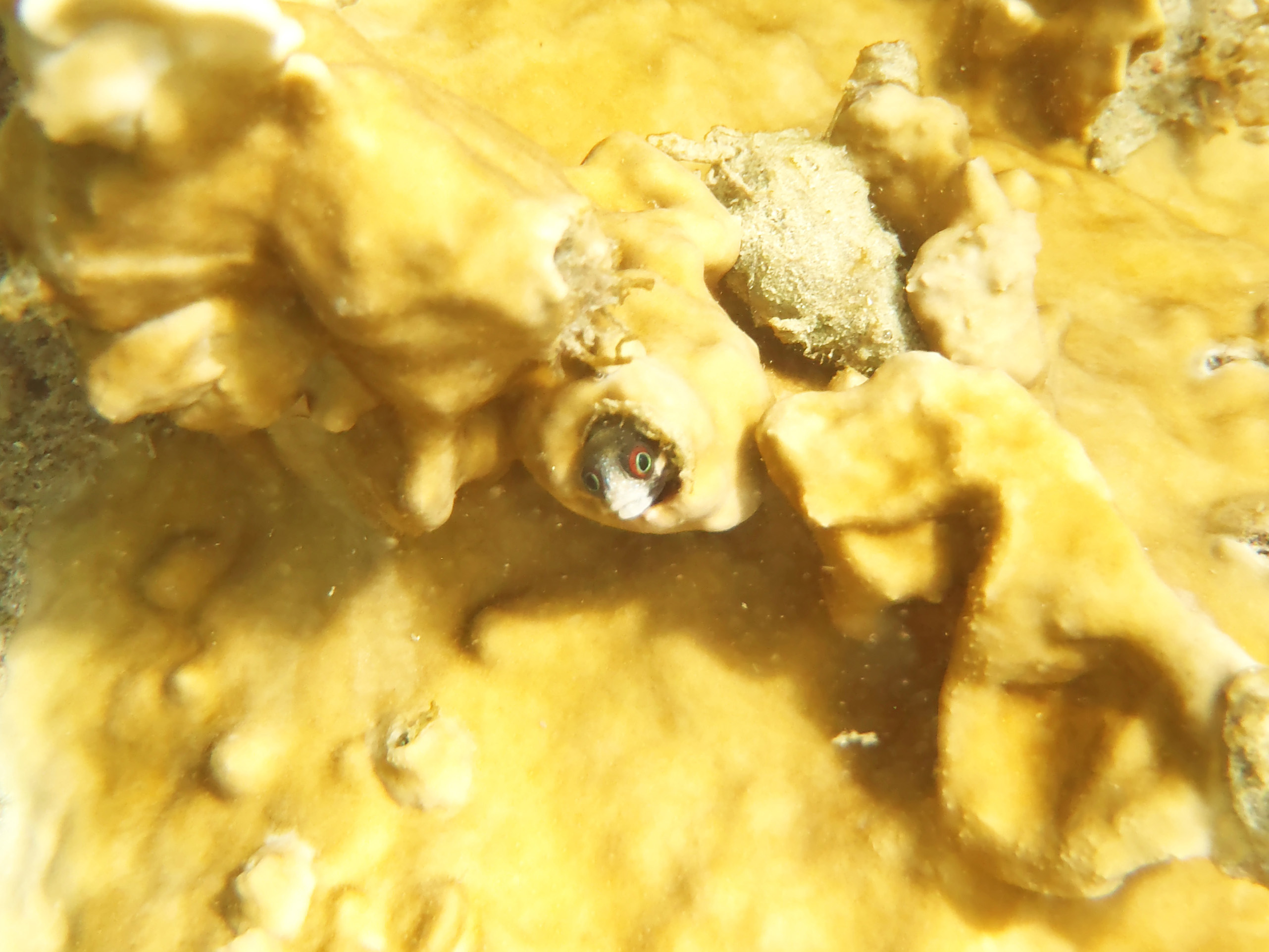
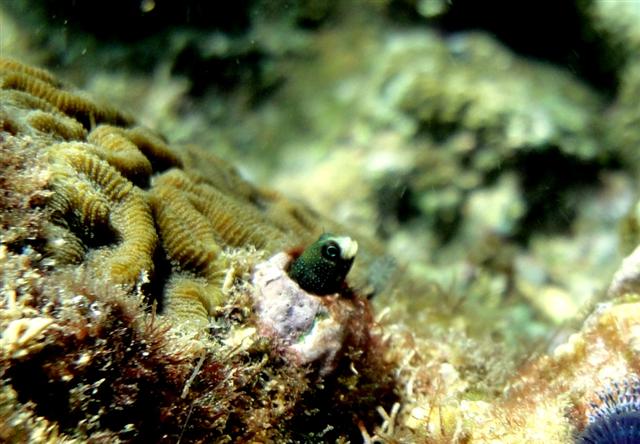
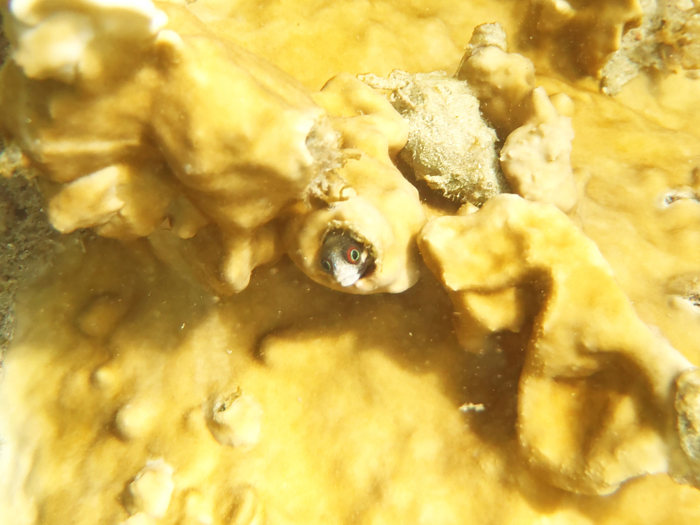
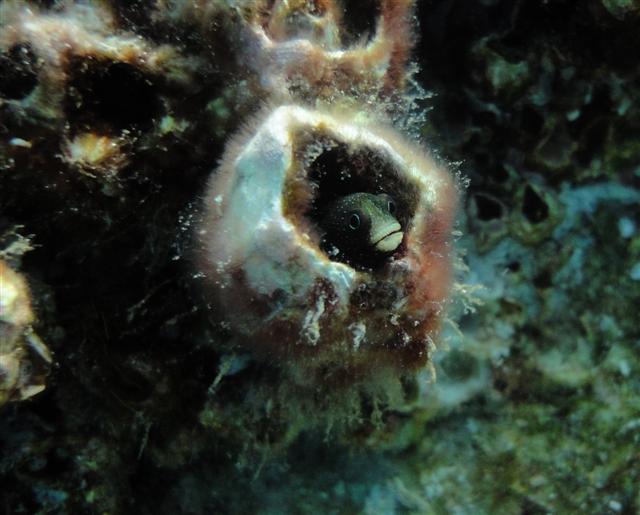
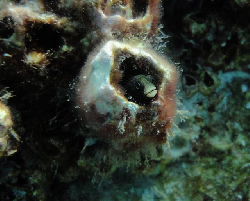
Acanthemblemaria rivasi Stephens, 1970
Description
Dorsal spines (total): 21 - 22; Anal spines: 2. Species distinguished by: dorsal-fin spines 21 or 22; total dorsal-fin elements 29 to 40; supraorbital cirrus simple, cranial spines short and blunt; patch of cranial spines on nape ends anterior to supratemporal commissural pore; inner rim of posterior infraorbital bone smooth; two or more rows of teeth on each palatine bone. Common amongst Chaenopsids: small elongate fishes; largest species about 12 cm SL, most under 5 cm SL. Head usually with cirri or fleshy flaps on anterior nostrils, eyes, and sometimes laterally on nape; gill membranes continuous with each other across posteroventral surface of head. Each jaw with canine-like or incisor-like teeth anteriorly; teeth usually also present on vomer and often on palatines (roof of mouth). Dorsal-fin spines flexible, usually outnumbering the segmented soft rays (numbering 7 to 37), spinous and segmented-rayed portions forming a single, continuous fin; 2 flexible spines in anal fin; pelvic fins inserted anterior to position of pectoral fins, with 1 spine not visible externally and only 2 or 3 segmented (soft) rays; all fin rays, including caudal-fin rays, unbranched (simple). Lateral line absent. Scales absent (Ref.52855).
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Teleostei
Order: Blenniiformes
Family: Chaenopsidae
Genus: Acanthemblemaria
Species: Acanthemblemaria rivasi Stephens, 1970
Climate Zone
Location
Biology
Life cycle and mating behavior
Habitat
associated
Conservation Status
Least Concern
Threat to Humans
Harmless